Fields
This article discusses various field types that NocoDB offers.
Fields define the structure and type of data stored in each record of a table. They are the building blocks of your database, determining how information is entered, displayed, and interpreted. Whether you're capturing names, numbers, dates, selections, or calculated values—fields provide the necessary flexibility to model your data accurately.
This section will guide you through the different types of fields available, their configurations, and best practices for choosing the right field type based on your use case. By understanding how fields work, you can design more effective tables and ensure consistent, meaningful data across your workspace.

Among all fields in a table, two hold special significance: the primary key and the display value. The primary key is a technical identifier that uniquely distinguishes each record and is essential for backend operations like updates, deletions, and maintaining data integrity. It is always unique and typically hidden from end users. On the other hand, the display value is a human-readable label—such as a name or title—used in the interface to help users quickly identify and associate records. While it’s recommended to use a field with unique values as the display value, strict uniqueness is not enforced. In essence, the primary key ensures consistent record management, while the display value improves usability and context.
Create a Field
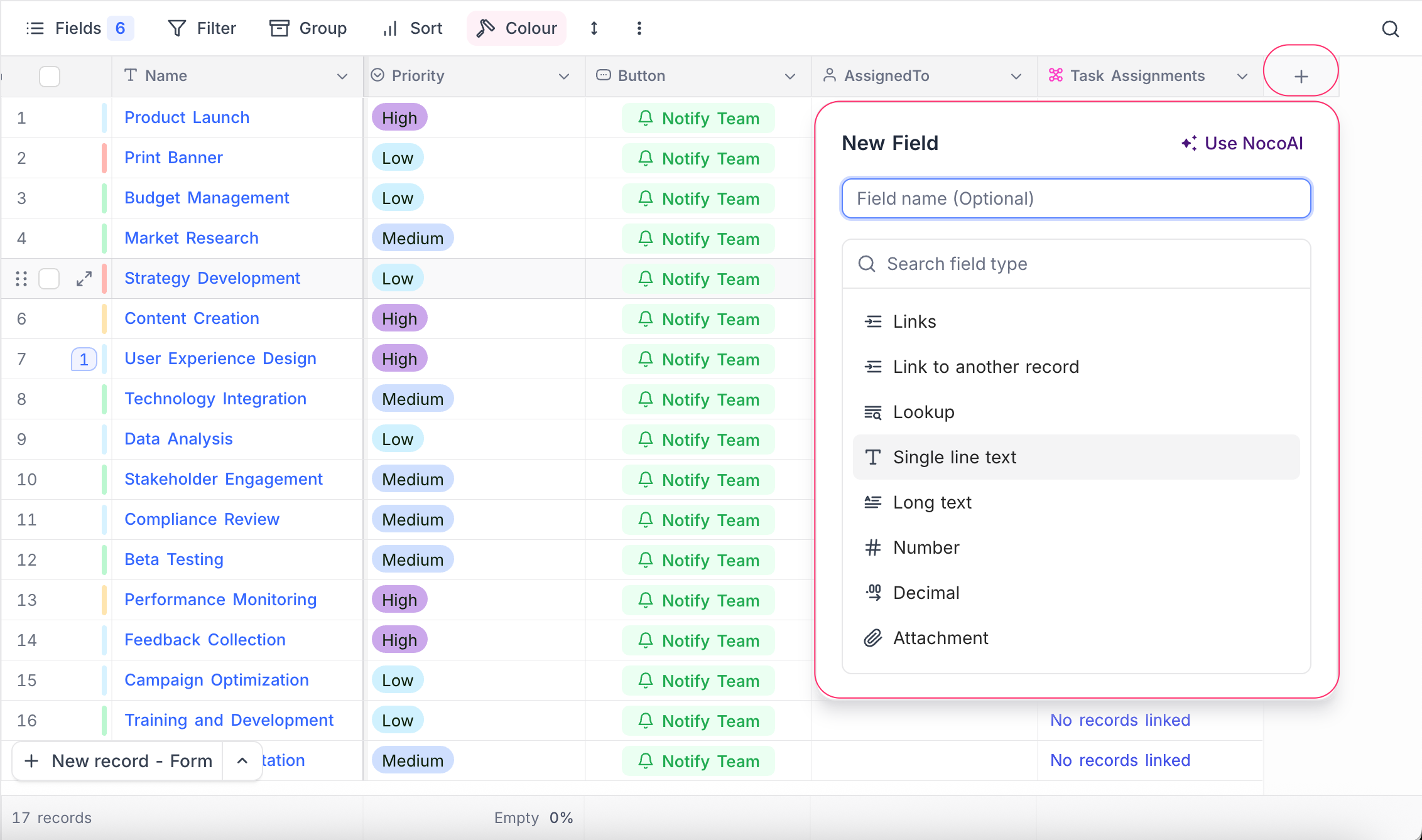
To add a new field to your table:
- Click on the ➕ icon in the table header where you'd like to insert the new field.
- In the New Field panel:
- Enter the field name (optional at first).
- Select the appropriate field type from the list (e.g., Single line text, Number, Lookup, etc.).
- Configure additional settings such as default value and description as needed.
- Unique constraints can be enabled for supported field types by checking the Unique values only option. More details can be found in the Unique Fields section below.
- Click Save Field to finalize the creation.
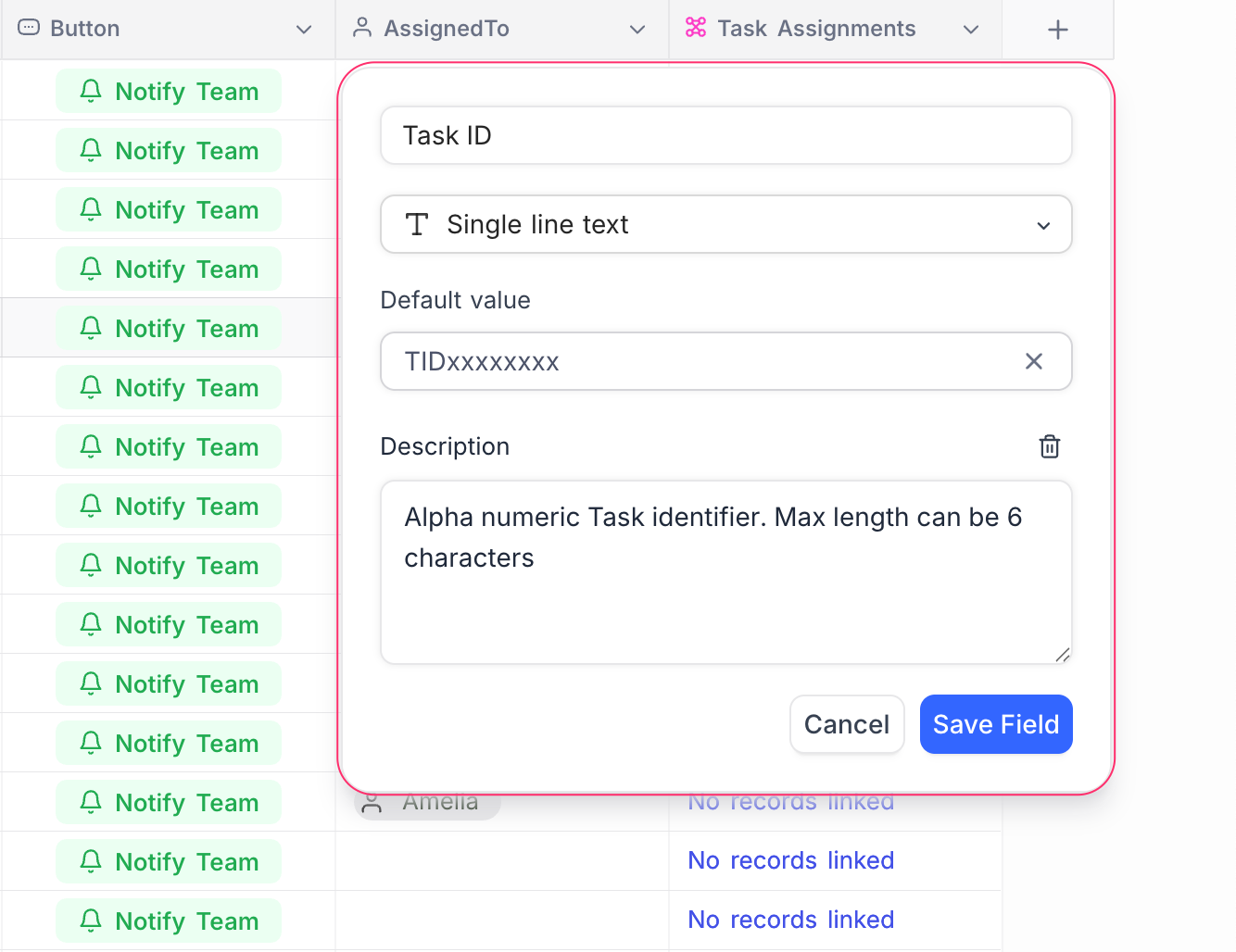
Depending on the field type selected, additional options or configurations may be required—such as allowed values, precision, formulas, or linked table settings. Refer to the documentation for each field type for detailed guidance.
Field Default Value
You can set a default value when creating a field. This value is automatically applied to new records created after the field is set. It does not affect existing records. The default can be a fixed value (e.g., "N/A", "Unknown") or, for some field types, a dynamic value such as the current date, time, or user ID. Refer Set default value for more details on how to configure default values.
Field Description

Adding a description to a field provides context and guidance for users interacting with the table. This is especially useful in collaborative environments where multiple users may access the same data. The description can include details about the field's purpose, expected values, or any specific instructions for data entry. It appears as a tooltip when users hover over i icon next to the field name in the table header. For more details, refer to Add/Edit Field Description.

Field Types
NocoDB offers a wide range of field types to help you structure your data effectively. From basic text and numeric fields to more advanced options like linked records, formulas, and custom types, each field serves a specific purpose. The table below provides an overview of all available field types along with brief descriptions to help you choose the right one for your use case.
| Field Type | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Text based | Single line text | For short text entries like names or titles. |
| Long text | Suitable for paragraphs or detailed notes. | |
| Stores and validates email addresses. | ||
| Phone | For storing phone numbers. | |
| URL | Stores website or web resource links. | |
| Numerical | Number | Whole numbers, positive or negative. |
| Decimal | Numbers with decimal precision. | |
| Percentage | Represents numeric values as percentages. | |
| Currency | Stores monetary values with currency symbol. | |
| Date & Time | Date | Captures calendar dates. |
| Time | Stores time of day. | |
| Date and time | Stores both date and time in one field. | |
| Duration | Measures length of time (e.g., hours or days). | |
| Select based | Single select | Allows choosing one option from a list. |
| Multi select | Allows selecting multiple options from a list. | |
| Link based | Links | Creates relationships between tables. |
| Lookup | Pulls data from linked records. | |
| Rollup | Aggregates values from related records. | |
| Custom types | Attachment | Upload and store files or images. |
| Barcode | Stores and displays barcodes. | |
| QR-code | Stores and displays QR codes. | |
| Geometry | For geographic or spatial data. | |
| JSON | Stores structured data in JSON format. | |
| Checkbox | Boolean toggle for true/false values. | |
| Rating | Displays star-based or numeric rating. | |
| Colour | Displays colour swatch & corresponding Hex code. | |
| Identifier | UUID | Auto-generates globally unique identifiers (UUID v4). |
| Formula | Formula | Computes values using expressions based on other fields. |
Unique Fields ☁
Certain field types in NocoDB can be configured to enforce uniqueness, ensuring that no two records contain the same non-empty value for that field. This is especially useful for fields such as email addresses, usernames, or other identifiers that must remain distinct across records. When enabled, empty cells are permitted, while duplicate non-empty values are prevented. You can enable this behavior by selecting the Unique values only option in the field settings during field creation or editing. Once configured, NocoDB validates all new entries and updates to enforce the uniqueness constraint.

When a user attempts to enter a duplicate value in a unique field, NocoDB will display an error message and prevent the record from being saved until a unique value is provided.
Supported field types for uniqueness enforcement include:
- Single line text
- Phone number
- URL
- Number
- Decimal
- Currency
- Percent
- DateTime
- Date
- Time
- Enforcing uniqueness can impact performance on large datasets. Enable this option only when required by your application.
- Uniqueness constraints are supported only for tables created within NocoDB (NC-DB). Fields from external database tables do not support uniqueness constraints via NocoDB.
- When converting an existing field to a unique field, all existing values must already be unique; otherwise, the conversion will fail.
- Default values and uniqueness constraints are mutually exclusive. A field marked as unique cannot have a default value.
- Empty values are allowed in unique fields and do not violate the uniqueness constraint.
Field Actions
Beyond selecting the right field type, you can also perform various actions to customize how fields behave and appear in your tables. These actions are accessible from the field’s context menu & toolbar menu and include:
- Rename a field
- Change field type
- Set default value
- Adjust field width
- Hide or unhide fields
- Set as display value
- Sort by field (ascending/descending)
- Duplicate a field
- Insert new field before or after
- Delete a field
- Add or edit field description
For step-by-step instructions and visuals, refer to the full guide on Actions on Field.